Diabetes Meal Plan
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the way the body processes blood sugar (glucose). It occurs when the body either doesn't produce enough insulin or cannot effectively use the insulin it does produce.
This leads to high blood sugar levels, which can cause long-term health complications if not properly managed.
Following a diabetes meal plan can help regulate blood sugar levels, prevent spikes, and reduce the risk of complications such as heart disease and nerve damage.
A balanced diabetes-friendly diet focuses on nutrient-dense foods, complex carbohydrates, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
At Zing Wellbeing, we provide tailored and customisable diabetes meal plans to help manage diabetes effectively, ensuring meals are high in fibre, low in added sugars, and balanced for blood sugar control.

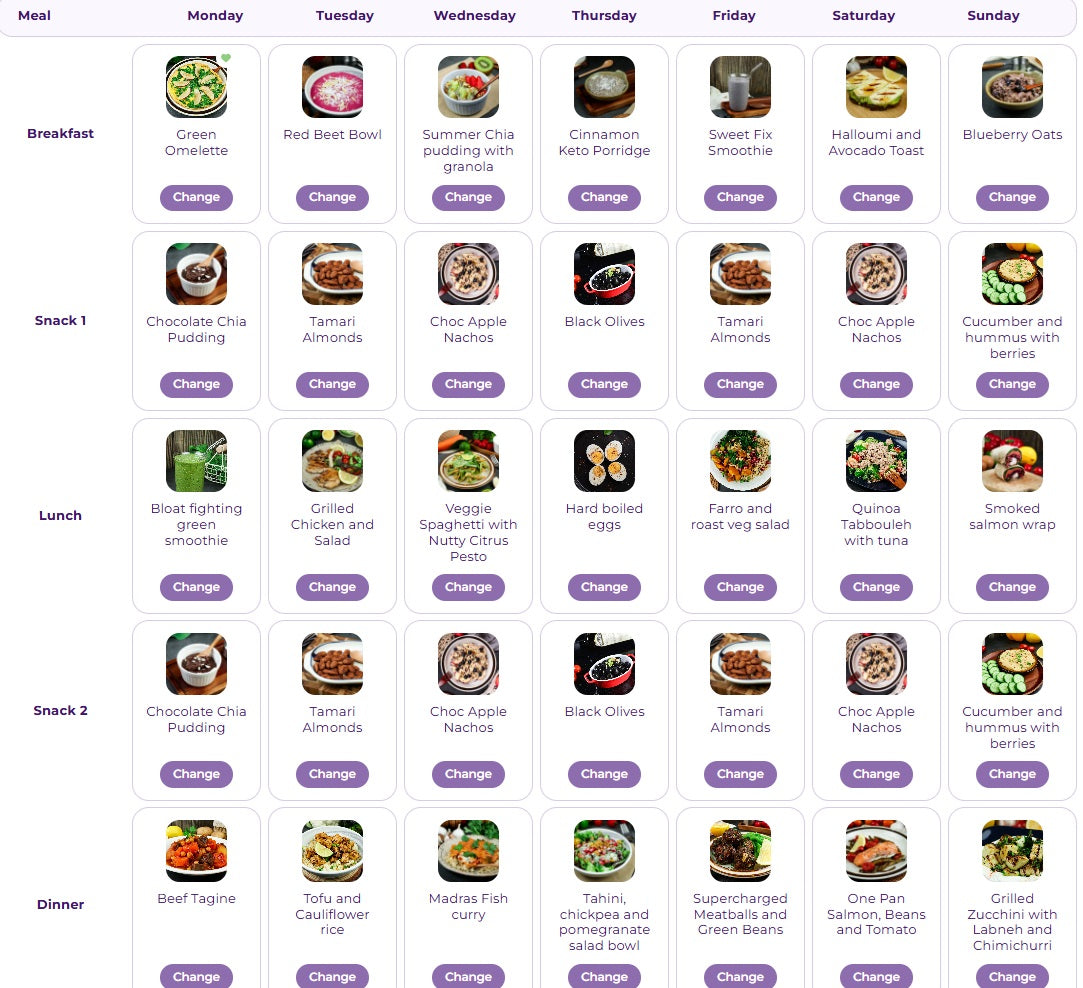
Diabetes meal plan
Eating for diabetes involves managing blood sugar levels through balanced nutrition, portion control, and regular meal timing. The Zing Wellbeing Diabetes meal plan is written with the following in mind:
1. Low-Glycemic Index (GI) Foods
Low glycemic index (GI) foods are those that cause a slow and steady rise in blood sugar levels after eating. The glycemic index measures how quickly a carbohydrate-containing food raises blood sugar levels on a scale of 0 to 100.
- Low GI foods: GI ≤ 55
- Medium GI foods: GI 56–69
- High GI foods: GI ≥ 70
Eating low GI foods is beneficial for managing blood sugar levels, maintaining energy, and reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications.
By including low GI foods we can control the rise of our blood sugar levels creating a slower, steadier rise and also reduce the risk of a blood sugar drop. We have include whole grains, quinoa, low starch vegetables, legumes and berries.
2. High Protein
A high-protein diet can benefit individuals with diabetes by improving blood sugar control, enhancing satiety, and supporting weight management.
Protein slows digestion and has little to no direct effect on blood sugar levels, unlike carbohydrates.
We have included quinoa, chicken, fish, eggs and tofu. For individuals on medications like insulin, adding protein to meals can reduce the risk of low blood sugar (hypoglycaemia) by slowing glucose absorption

3. Healthy Fats
Including healthy fats in your diet is beneficial for managing diabetes as they help improve insulin sensitivity, promote heart health, and provide lasting energy.
Unlike unhealthy fats, which can worsen inflammation and insulin resistance, healthy fats support overall metabolic health. We have included avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil and fish.

4. No added sugar
We have hit that sweet spot with natural sweet foods like whole fruit (with the skin on) and natural sweeteners.
One of the most significant advantages of cutting sugar is its impact on metabolic health. Excessive sugar consumption, particularly fructose, has been linked to insulin resistance, a precursor to type 2 diabetes.
By detoxing from sugar, insulin sensitivity can improve, helping the body manage blood sugar levels more effectively.
Reducing sugar also helps decrease fat storage, particularly visceral fat, which is associated with metabolic syndrome and heart disease.
Sugar is calorie-dense and provides little nutritional value, contributing to excess caloric intake and weight gain.


